Table of Contents
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
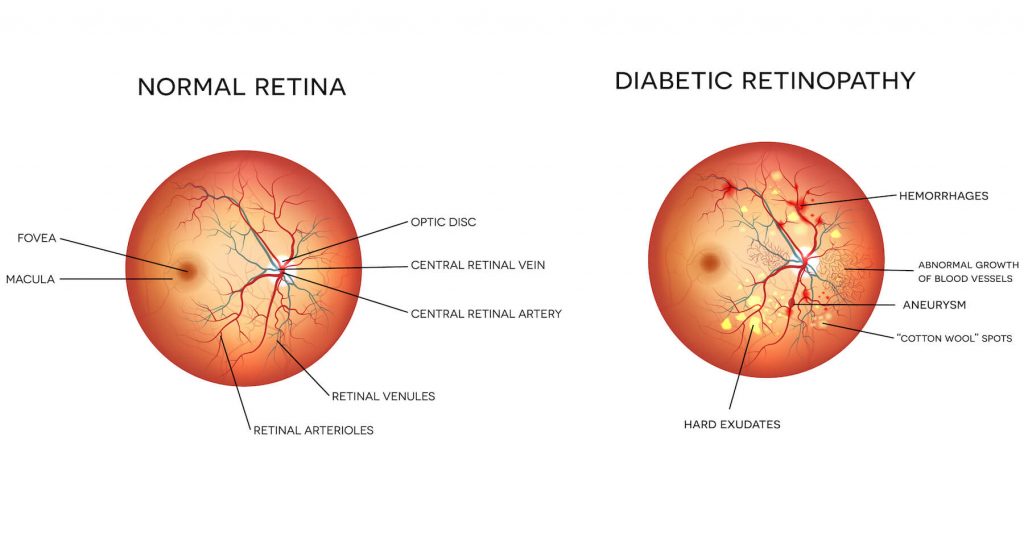
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye disease that can occur in people with diabetes mellitus. It results from high sugar levels in diabetic patients. High levels of sugar for a prolonged period of time causes damage to fine blood vessels in the entire body, including the retina of the eyes. The retina’s function is to detect light and then send signals to the brain via the optic nerve of the eye.
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when high sugar levels cause abnormal leakage as well as blockage of tiny blood vessels. As a response to poor oxygenation of the retina, new blood vessels may grow in the eyes, but these vessels are likely to be weak and can bleed more easily. If new blood vessels start to grow in the eye, the condition is referred to as proliferative diabetic retinopathy. This is an advanced stage of the disease and has a high risk of vision loss.
Fluid may also accumulate in the macula due to high levels of sugar in the bloodstream. This is known as diabetic macular oedema.
High sugar levels can also change the shape as well as the curvature of the lens, which leads to blurred vision.
Symptoms
Diabetic retinopathy can become advanced even before it causes symptoms. The effect of the disease is seen on both eyes, but can be asymmetric. Some of the signs and symptoms include:
- Blurred vision
- Colour vision impairment
- Reduced night vision
- Floaters – these are dark strings or transparent spots that may float in the field of vision of the person with the disease, usually due to bleeding into the vitreous cavity.
- A blind spot in the centre of vision
- A sudden and total loss of eyesight

Risk Factors
Any person who has been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus is at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. However, the risk increases if the following cases are present in the person:-
- The blood sugar levels are uncontrolled
- Blood pressure levels tend to be in the higher range
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- A patient has been diabetic for several years
- Pregnancy
Diagnosis
As mentioned before, there are usually no noticeable changes to vision in the initial stages of the development of the disease. However, an ophthalmologist, an eye specialist, is trained to detect any such signs and symptoms.
It is of utmost necessity that diabetic patients get their eye tests performed regularly, for early detection of any such underlying problems. Some of the methods or tests conducted to detect and diagnose diabetic retinopathy include dilated retinal examination, fluorescein angiography, and optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Treatment
The treatment of diabetic retinopathy depends on the stage and type of disease.
Optimal control of sugar levels can slow down and even reverse diabetic retinopathy. In the early stages, an ophthalmologist may monitor the condition of the eyes.
In advanced diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema, specialised treatment is usually needed. Treatment options include:
- Laser treatment – to reduce the risk of retinal detachment and vision loss.
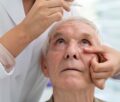
- Intra-vitreal injection of anti-VEGF drugs, e.g. Eylea, Lucentis, Avastin. These injections are given into the eye under local anaesthesia.
- Vitrectomy surgery – for advanced stages and bleeding inside the eye.
Prevention
Besides preventing the disease, controlling blood sugar levels can help reduce diabetic retinopathy and make treatments much more effective. Early detection can also help in making treatment more effective.
Some recommendations for diabetic patients are:
- Consuming a healthy and balanced diet
- Regular physical activity and exercise
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Quit smoking
- Controlled alcohol consumption
- Regular eye checkups and treatments
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy is a treatable eye disease that can be prevented, and controlled if detected at an early stage. However, if not treated in time, it can lead to serious consequences such as loss of vision. It is therefore important to have regular visits to your ophthalmologist.
Dr Parth Shah is an ophthalmologist in Canberra who specialises in treating eye diseases in patients of all ages. He has affiliations with renowned hospitals and medical institutions, and is committed to providing the highest level of care for all of his patients, using the latest technology.