Table of Contents
Blunt eye trauma is a serious injury that can cause permanent damage to the eye.
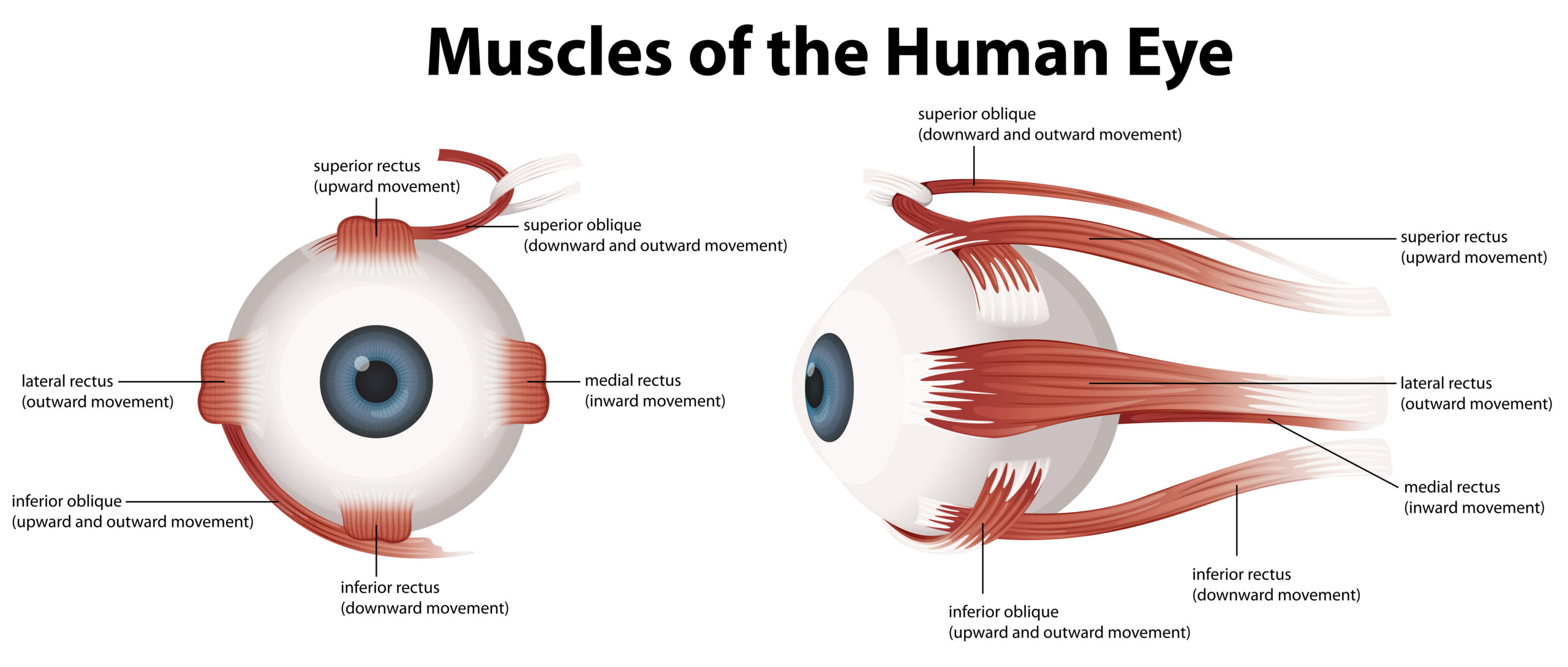
Blunt eye trauma can cause damage to the globe (eyeball), bones of the eye socket, and the eyelid. This can lead to vision problems and pain.
The ocular injuries that can occur as a result of a fall or other physical trauma to the eye are often sudden and dramatic. The eyeball is compressed and distorted, which can lead to vision loss and other medical problems.
Symptoms of Blunt Eye Trauma
Blunt eye trauma can cause a number of symptoms, depending on the severity of the injury.
- Pain and Discomfort
- Swelling
- Bruising or Black Eye
- Blurred Vision
- Redness
- Tearing and Sensitivity to Light
- Double Vision
- Foreign Body Sensation
- Decreased Eye Movement
- Visible Damage
- Deformity of the eye socket
- Numbness around the eye
- Abnormal upper eyelid movement
- Eye deformity

What Causes Blunt Eye Trauma?
Blunt eye trauma can be caused by a sudden impact to the eye.
Common causes of blunt eye trauma include:
- Sports Injuries
- Accidents and Falls
- Assaults and Physical Altercations
- Workplace Injuries
- Accidental Household Injuries
- Recreational Activities
- Childhood Accidents
Blunt eye trauma is a medical condition that is most commonly experienced by young men. 95% of ocular trauma injuries occur in men under 30 years of age, often caused by interpersonal violence. Blunt trauma can cause a variety of serious medical conditions, including blindness.
What to Do After a Blunt Eye Injury
Blunt eye trauma is a serious injury that can result in vision loss if not treated quickly. Symptoms of blunt eye trauma include a sudden decrease in vision, pain, and redness. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should consult with an ophthalmologist as soon as possible. By treating the injury quickly, you can reduce your risk of vision loss.
Here’s what you should do if you’ve suffered blunt eye trauma:
● Avoid touching your eyes until after you receive treatment
● If you are bleeding, apply pressure with clean cloth or gauze pads
Blunt Eye Trauma Diagnosis
Diagnosing blunt eye trauma involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional. Here are some key aspects of the diagnosis process:
- Patient History: The healthcare provider will inquire about the details of the injury, including how it occurred, the force of impact, and any symptoms experienced. Pre-existing medical conditions, medications, and allergies will also be considered.
- Visual Acuity Testing: An assessment of visual acuity using an eye chart helps determine the extent of vision loss, if any.
- External Examination: The eye and surrounding structures will be examined for signs of swelling, bruising, or lacerations. Any abnormalities in eyelid position, pupil size, or eye movement will be noted.
- Intraocular Pressure Measurement: Intraocular pressure may be measured to assess for conditions such as glaucoma, which can be exacerbated by trauma.
- Slit Lamp Examination: A slit lamp is a specialised microscope that allows for detailed examination of the cornea, lens, and other anterior eye structures.
- Dilated Fundus Examination: By dilating the pupils, the healthcare provider can examine the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels at the back of the eye for signs of damage.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI may be ordered to assess for fractures, foreign bodies, or other internal damage.
- Specialised Tests: Additional tests, such as ultrasound or fluorescein angiography, may be conducted based on the specific suspected injuries.
- Neurological Assessment: Since blunt eye trauma can be associated with head injuries, a neurological assessment may be performed to check for signs of concussion or other brain-related issues.
- Follow-up Evaluations: Periodic re-evaluations may be necessary to monitor for delayed complications or changes in symptoms.
Treatment For Blunt Eye Trauma
Treatment of blunt trauma depends entirely on the extent of the injury.
Treatment for mild blunt eye trauma includes:
- Avoid rubbing the eye.
- Do not apply pressure.
- Do not attempt to rinse the eye.
- Minimise movement.
- Steroid eye drops to reduce inflammation.
- Rest.
- Avoid using aspirin and ibuprofen as they have the potential to enhance bleeding.
- Antiemetics or anti-nausea medication.
- Wearing protective eyewear.
- Follow-up eye examinations.
Potential Complications of Blunt Eye Trauma
Blunt eye trauma can lead to various complications, depending on the severity and location of the injury. Some potential complications include:
- Corneal Abrasion or Laceration
- Hyphema
- Traumatic Iritis
- Lens Dislocation or Cataract
- Retinal Detachment
- Orbital Fractures
- Optic Nerve Damage
- Concussion or Traumatic Brain Injury
- Secondary Infections
- Traumatic Glaucoma
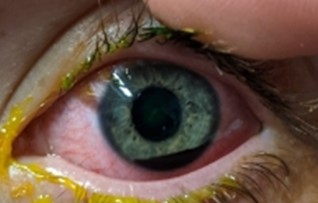
A hyphaema (layer of blood) inside the eye, it is located between the cornea and iris.
If you experience a sudden decrease in vision, or a severe headache, contact your nearest eye doctor immediately. Blunt trauma can lead to vision loss, and if left untreated, can lead to blindness.
Possible Long-Term Effects of Blunt Eye Trauma
Blunt eye trauma can have various long-term effects depending on the severity and specific nature of the injury. It’s crucial to note that any eye injury should be promptly evaluated and treated by an eye care professional to minimise potential complications. Here are some possible long-term effects of blunt eye trauma:
- Visual Impairment
- Retinal Detachment
- Cataracts
- Glaucoma
- Corneal Injuries
- Conjunctival Damage
- Strabismus
- Secondary Infections
- Psychological Impact
- Eye pain
- Cosmetic effects
How to Prevent Blunt Eye Trauma
Preventing blunt eye trauma involves taking precautions and being mindful of potential risks. Here are some practical tips to help reduce the risk of blunt eye injuries:
- Wear Protective Eyewear
- Use Seat Belts and Airbags
- Childproof the Home
- Be Cautious with Tools and Equipment:
- Practise Safe Sport
- Be Mindful of Surroundings
- Regular Eye Check-ups
- Teach children about the importance of eye safety and proper behaviour to avoid accidents
- Follow Workplace Safety Guidelines
Summary
If you suffer from blunt eye trauma, you should seek medical attention from the nearest ophthalmologist as soon as possible. Blunt eye trauma can cause permanent damage to the eyes, and if not treated, it can lead to blindness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can blunt force trauma cause blindness?
Yes, blunt force trauma can cause blindness
Can you go blind from getting hit in the day?
People participating in high-risk occupations and sports should exercise extreme caution and wear protective eyewear.
Can getting hit in the eye cause retinal detachment?
How long does it take for eye trauma to heal?
Do eyeballs heal themselves during blunt eye trauma?
What are the long-term implications for eye health after blunt eye trauma?
Is there a difference between blunt eye trauma and penetrating eye injuries?
Are children more susceptible to blunt eye trauma?
Is there a link between blunt eye trauma and the development of eye conditions like glaucoma or cataracts later in life?
Author Bio
Dr Parth Shah is an experienced ophthalmologist in Canberra, specialising in cataract surgery. With extensive training and experience, he is renowned for his expertise in the field. Dr Shah is dedicated not only to performing successful surgeries but also to patient education. His compassionate approach, combined with technical proficiency, has earned him the trust and gratitude of countless patients. He is a true advocate for eye health and a trusted name in the Canberra ophthalmology community.