Table of Contents
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of eye injections, shedding light on their types, benefits, risks, procedure, and much more.
What Are Eye Injections?
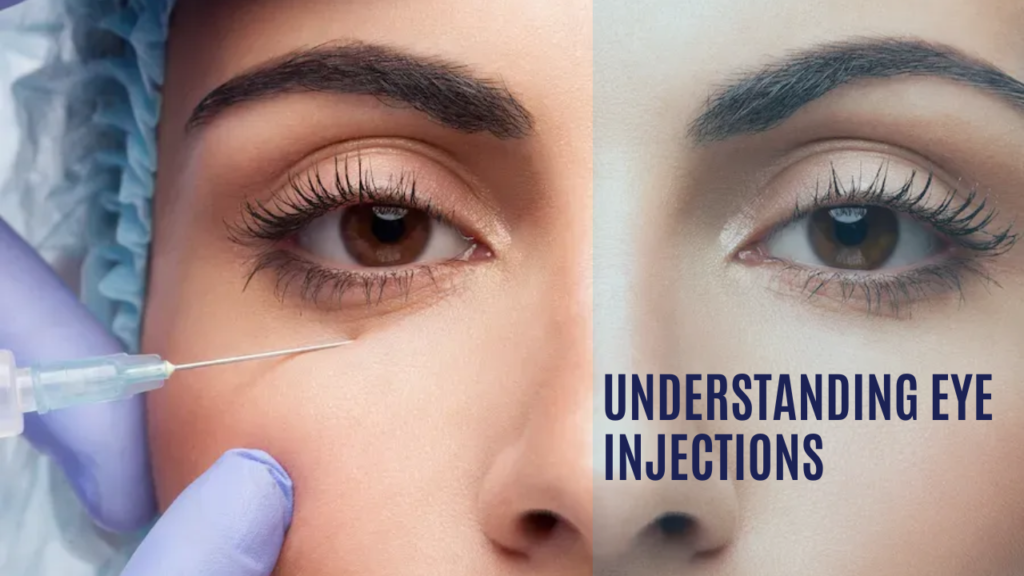
Eye injections, as the term suggests, involve the delivery of medication directly into the eye through an injection. This targeted approach ensures that the medication reaches its intended destination swiftly, bypassing barriers that eye drops and oral medications might face in the body. This method is particularly valuable when treating conditions that affect the back of the eye, such as the retina.
Eye Conditions Requiring Injections
Our eyes are precious windows to the world, and protecting them is paramount. Some eye conditions, if left untreated, can lead to irreversible damage. That is where eye injections come into play. These injections have emerged as a remarkable solution for managing several critical eye conditions. Let’s delve into some of these conditions:
1. Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD):
Age-related macular degeneration is a leading cause of vision loss among the older population. It primarily affects the macula, the central portion of the retina responsible for sharp and detailed vision. Intravitreal injections of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) medications, such as ranibizumab, bevacizumab, and aflibercept, have revolutionised the treatment of AMD. These injections help suppress abnormal blood vessel growth and leakage, aiming to preserve central vision and preventing further deterioration.
2. Diabetic Retinopathy:
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that affects the blood vessels in the retina. In cases of proliferative diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema, where abnormal blood vessel growth occurs, anti-VEGF injections can help reduce vascular leakage and control neovascularisation, thus reducing the risk of vision-threatening complications.
3. Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO):
Retinal Vein Occlusion occurs when a blood clot blocks a retinal vein, leading to retinal swelling and potential vision loss. Intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF agents have shown promising results in managing macular oedema associated with RVO, improving visual outcomes and reducing macular thickness.
4. Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP):
ROP primarily affects premature infants and occurs due to abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina. Anti-VEGF injections have emerged as a potential treatment option for severe cases of ROP, aiding in the regression of abnormal vessels and promoting healthier retinal development.
5. Uveitis:
Uveitis is characterised by inflammation of the uveal tract of the eye and can lead to vision loss if left untreated. Intravitreal corticosteroid injections offer targeted anti-inflammatory treatment, helping to control the inflammation and preserve visual function.
6. Neovascular Glaucoma:
Neovascular glaucoma is a severe form of glaucoma characterised by abnormal blood vessel growth on the iris and internal drainage angle. Intravitreal anti-VEGF injections can help reduce neovascularisation, which in turn helps manage intraocular pressure and prevent further optic nerve damage.
Types of Eye Injections
1. Anti-VEGF Injections
Anti-VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) injections are a remarkable advancement in ophthalmology. These injections work by inhibiting the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the eye, a common occurrence in conditions like age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic retinopathy. By halting this abnormal growth, these injections can prevent further vision loss and even improve vision in some cases.
2. Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections are used to manage inflammation in the eye. Inflammation can lead to conditions like uveitis and macular oedema, which can severely impact vision. Corticosteroids reduce inflammation and can help control these conditions effectively. While they offer relief, potential risks and side effects, such as increased intraocular pressure, should be considered.
3. Antibiotic Injections
For eye infections that require targeted treatment, antibiotic injections are a powerful solution. These injections deliver antibiotics directly to the infection site, which can be crucial in cases of severe infections like endophthalmitis.
The Procedure Step by Step:
The eye injection procedure is typically performed in an outpatient setting and involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The eye is numbed with topical anaesthesia to minimise discomfort during the procedure.
- Asepsis: The eye and its surrounding area are cleaned with and antiseptic solution to reduce the risk of infection.
- Medication Administration: Using a fine needle, the ophthalmologist carefully delivers the medication into the vitreous humour of the eye. Specialised imaging techniques, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT), may be used to guide the frequency of injections.
- Post-Injection care: Patients are given specific instructions for post-injection care.
Benefits and Risks
Benefits of Eye Injections
- Eye injections provide targeted treatment for various eye conditions.
- These injections deliver medication precisely where it’s needed in the eye.
- Eye injections can help prevent disease progression and vision loss.
- Many patients experience improved vision and quality of life.
- Eye injections are minimally invasive and generally well-tolerated.
- Regular injections may be recommended to maintain long-term eye health.
- Customised treatment plans ensure optimal results for each patient.
Risks and Side Effects
- Some patients might experience temporary discomfort or pain during or after the injection.
- The eye may be red from external bleeding.
- There is small chance of bleeding inside the eye, which can affect vision.
- Eye injections carry the risk of infection at the injection site.
- Rarely, patients may encounter retinal detachment, leading to potential vision loss.
- There is a small risk of cataract formation due to certain medications used in injections.
- Inflammation inside the eye is a possible side effect, which can impact vision clarity.
- Although rare, allergic reactions to injected medications can occur.
- Eye injections might cause floaters or visual disturbances in some cases.
- Patients could experience an elevation in intraocular pressure, requiring monitoring.
Dr. Parth Shah’s expertise ensures precise administration, minimising the risk of complications and promoting healing.
What to Expect After the Injection
- Mild Discomfort: You might experience mild discomfort or a scratchy sensation in your eye after the injection.
- Watery Eyes: It is normal for your eyes to water more than usual for a short period after the injection.
- Blurry Vision: Your vision may be blurry immediately after the injection, but this should improve within a few hours.
- Avoid Touching: Try not to touch or rub your eyes, as this could increase the risk of infection.
- Rest Afterward: It’s a good idea to rest for a little while after the injection to allow your eye to recover.
- Sunglasses: Wear sunglasses when you go outside to protect your eyes from light sensitivity.
- Follow-Up Instructions: Your doctor will provide specific instructions for any post-injection care, so be sure to follow them carefully.
- Possible Redness: Some redness around the injection site is normal and should subside over time. A subconjunctival haemorrhage is also common, and takes a few days to resolve.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are eye injections painful?
What types of medications are delivered through eye injections?
How are the injections administered?
How frequently will I need eye injections?
Are there any risks or side effects associated with these injections?
What should I expect after the injection?
Are there any restrictions following the procedure?
How do I know if eye injections are working for me?
What should I discuss with my ophthalmologist before getting an eye injection?
Conclusion
In the world of ophthalmology, eye injections have emerged as a powerful tool for preserving and restoring vision. By understanding the benefits, risks, and procedure of eye injections, you can approach your treatment journey with confidence, knowing that you’re in the hands of a skilled and compassionate professional.