Table of Contents
Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) is a condition that affects the blood vessels in the retina of the eye, and can lead to vision loss. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of RVO to help you better understand this condition.
What is Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO)?
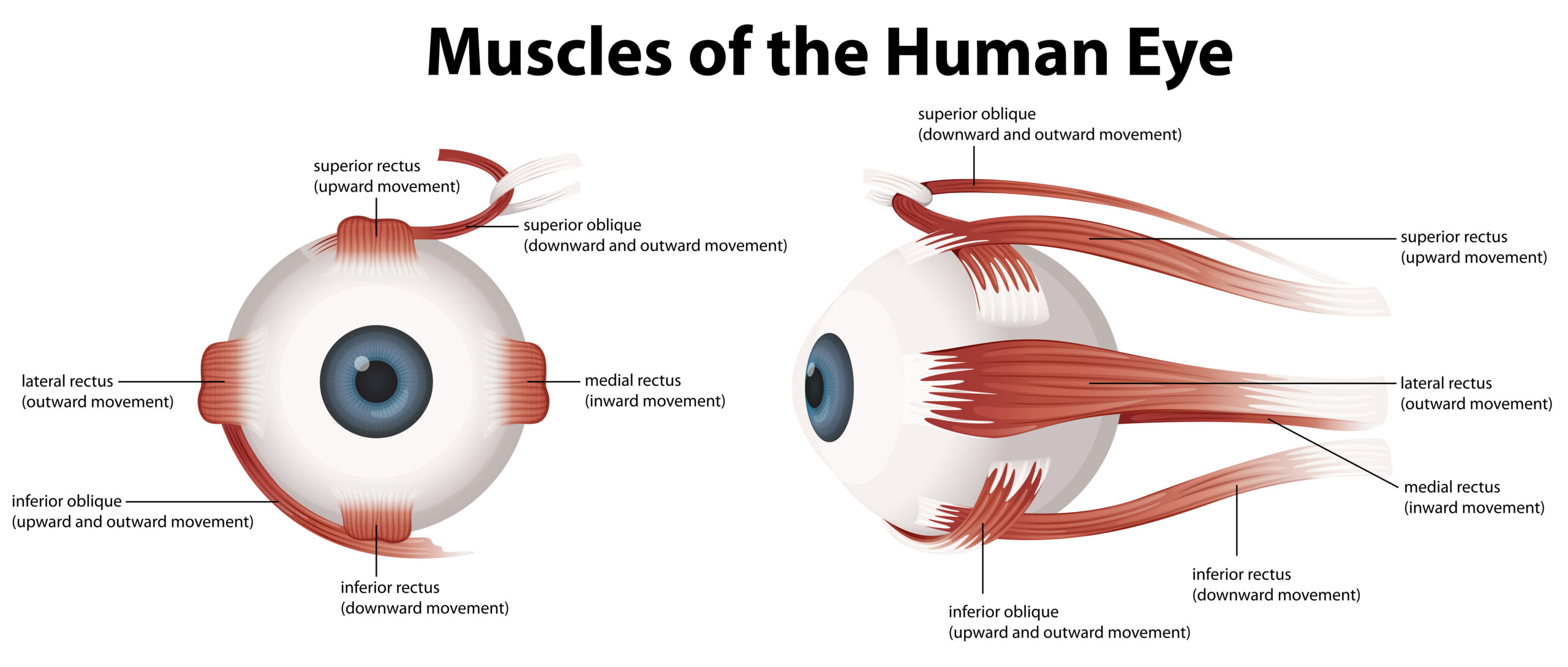
Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) is a condition where one or more veins that carry blood away from the retina become obstructed, leading to the swelling of the veins and the leakage of blood into the retina, which can cause vision loss.
Causes of Retinal Vein Occlusion?
Retinal vein occlusion occurs when a blood clot forms in one of the retinal veins, blocking the flow of blood and causing swelling in the retina. There are two types of RVO:
1. Central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO) – This occurs when the main (central) retinal vein is blocked, and affects the entire retina.
2. Branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) – This occurs when one of the smaller veins branching off the main vein is blocked, and affects part of the retina.
Risk factors of Retinal Vein Occlusion
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing RVO, includingHigh blood pressure
● High cholesterol
● Diabetes
● Glaucoma
● Smoking
● History of blood clots
● Heart disease
● Stroke
● Eye inflammation
What are the Symptoms of Retinal Vein Occlusion?
The symptoms of RVO can vary, depending on the severity of the blockage and the type of RVO. Common symptoms include:Blurred or distorted vision
● Loss of peripheral vision
● Dark or empty spots in your vision
● Sensitivity to light
● Eye pain or discomfort

If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek eye doctor consultation immediately. Your ophthalmologist can perform a comprehensive eye exam and recommend the best course of treatment.
How is Retinal Vein Occlusion Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Retinal Vein Occlusion usually involves a comprehensive eye examination. Your eye doctor will dilate your pupils and examine your retina and blood vessels using a special magnifying lens. They may also perform a fluorescein angiography, which involves injecting a dye into your arm and taking a series of photographs of your eye to assess the extent of the blockage.
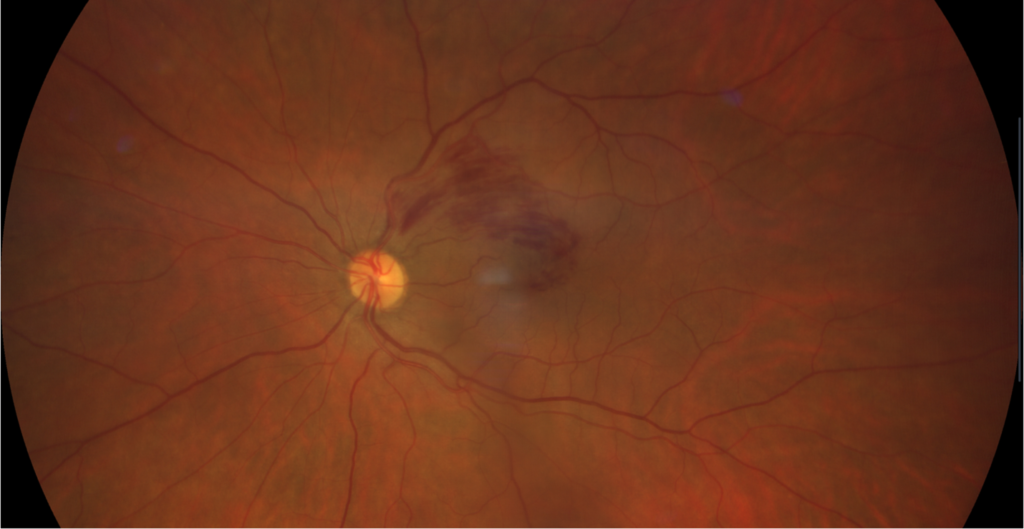
A retinal photo of branch retinal vein occlusion with numerous flame-shaped haemorrhages (bleeds) in the upper portion of the left macula.
What are the Treatment Options for Retinal Vein Occlusion?
The treatment for RVO will vary based on the type and severity of the condition. In many cases, the condition may resolve on its own without the need for treatment. However, when necessary, treatment options include:
Anti-VEGF injections: This involves injecting a medication into the eye to decrease swelling and improve vision.
Laser treatment: This involves using a laser to seal leaking blood vessels in the retina.
Corticosteroids: This involves using steroid medication to reduce inflammation and improve vision.
Surgery: In certain cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the blockage in the vein.
It is crucial to discuss the available treatment options with your eye doctor to determine the most suitable course of action for your particular situation.
Can Retinal Vein Occlusion be Prevented?
Although there is no guaranteed way to prevent RVO, there are measures you can take to decrease your risk of developing the condition. These include:Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise routine.
● Managing high blood pressure and cholesterol.
● Controlling diabetes.
● Quitting smoking.
● Visiting your eye doctor for regular check-ups.
FAQs:
Is retinal vein occlusion curable?
Can retinal vein occlusion lead to permanent blindness?
Can retinal vein occlusion occur in both eyes?
Conclusion:
Retinal vein occlusion is a serious eye condition that can lead to vision loss if left untreated. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned in this article, it is essential to consult an eye doctor immediately. Early detection and treatment can prevent vision loss and help preserve your vision. Remember to maintain a healthy lifestyle and manage any underlying health conditions to reduce your risk of developing retinal vein occlusion.